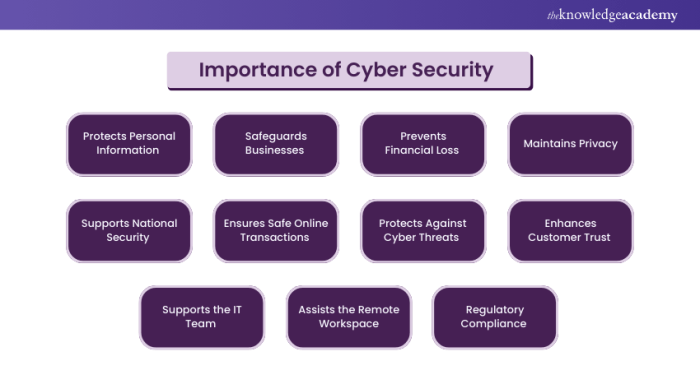
Exploring the pivotal role of cybersecurity in protecting digital identities, this article sheds light on the importance of staying secure in the digital realm.
Delving into the realm of cyber threats and their potential impact on digital identity, we uncover the repercussions of overlooking cybersecurity measures.
Importance of Cybersecurity in Digital Identity Management
In today’s digital age, where personal information is stored and shared online, cybersecurity plays a crucial role in protecting digital identities from various threats.
Role of Cybersecurity in Protecting Digital Identities
Cybersecurity measures are essential to safeguarding digital identities against unauthorized access, data breaches, and identity theft. By implementing robust security protocols, organizations can ensure that sensitive information remains confidential and secure.
Examples of Cyber Threats that Can Compromise Digital Identity
- Phishing attacks: Cybercriminals use deceptive emails or websites to trick individuals into providing their personal information, such as login credentials or financial details.
- Malware: Malicious software can infect devices and steal sensitive data, compromising digital identities.
- Identity theft: Hackers can steal personal information to impersonate individuals online, leading to financial loss and reputational damage.
Consequences of Inadequate Cybersecurity Measures in Digital Identity Management
- Data breaches: Without proper cybersecurity measures, sensitive information can be exposed, leading to financial loss and reputational damage for individuals and organizations.
- Legal implications: Inadequate cybersecurity can result in non-compliance with data protection regulations, leading to fines and legal consequences.
- Loss of trust: A breach of digital identities can erode trust between individuals and organizations, impacting relationships and business operations.
Strategies for Ensuring Cybersecurity in Digital Identity Management

In order to safeguard digital identities against cyber threats, it is essential to implement a range of best practices and security measures. These strategies play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information.
Best Practices for Securing Digital Identities
- Implementing strong password policies: Encouraging the use of complex passwords and regular password updates can help prevent unauthorized access.
- Utilizing encryption techniques: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit can add an extra layer of protection against cyber threats.
- Regular security audits: Conducting periodic audits to identify vulnerabilities and address potential security gaps is essential for maintaining a secure digital environment.
- Employee training and awareness: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices and raising awareness about potential threats can help prevent security incidents.
Comparison of Authentication Methods
- Biometric authentication: Utilizing biometric identifiers such as fingerprints or facial recognition can enhance security by providing unique and difficult-to-replicate authentication factors.
- One-time passwords (OTPs): Implementing OTPs through SMS or authenticator apps can add an extra layer of security by requiring a temporary code for authentication.
- Smart cards and tokens: Using physical tokens or smart cards for authentication can help prevent unauthorized access by requiring a physical object in addition to a password.
Insights on Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication
- Enhanced security: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) combines multiple authentication factors to verify the identity of users, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Implementation considerations: When implementing MFA, it is important to consider user experience, scalability, and integration with existing systems to ensure seamless authentication processes.
- Adaptive MFA: Implementing adaptive MFA can provide additional security by adjusting authentication requirements based on user behavior, location, or other contextual factors.
Technologies Shaping Cybersecurity in Digital Identity Management
In the realm of digital identity management, emerging technologies play a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity measures. Technologies like blockchain, AI, machine learning, and biometrics are revolutionizing the way organizations secure digital identities and sensitive information.
Blockchain and Its Impact
Blockchain technology is transforming cybersecurity in digital identity management by offering decentralized and immutable data storage. By creating a tamper-proof record of transactions and interactions, blockchain enhances security and reduces the risk of data breaches. This technology ensures that digital identities are securely stored and accessed only by authorized individuals, thereby safeguarding sensitive information.
AI and Machine Learning for Strengthening Security
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being leveraged to strengthen cybersecurity measures in digital identity management. These technologies enable organizations to detect and respond to security threats in real-time, identify patterns of suspicious behavior, and predict potential risks before they escalate.
By continuously learning and adapting, AI and machine learning algorithms enhance security by providing proactive defense mechanisms against cyber attacks.
The Role of Biometrics in Enhancing Security
Biometrics, such as fingerprint scans, facial recognition, and iris scans, are playing a crucial role in enhancing security in digital identity management. By using unique physical characteristics for authentication purposes, biometrics provide an additional layer of security beyond traditional passwords and PINs.
This technology ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information, making it harder for cybercriminals to compromise digital identities.
Compliance and Regulations in Cybersecurity for Digital Identity Management
Compliance with regulations is a critical aspect of cybersecurity for digital identity management. It ensures that organizations follow specific rules and guidelines to protect sensitive data and maintain trust with their customers.
Key Regulations and Their Influence
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a key regulation that significantly impacts cybersecurity practices in digital identity management. It mandates strict requirements for data protection, including the need for consent, data minimization, and breach notification.
- Compliance with GDPR not only helps in protecting personal data but also enhances cybersecurity measures by enforcing stringent protocols for data handling and storage.
- Other regulations like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) also play a crucial role in shaping cybersecurity practices in digital identity management.
Importance of Compliance with Data Protection Laws
Ensuring compliance with data protection laws is essential for maintaining cybersecurity in digital identity management. Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences such as hefty fines, legal actions, and reputational damage.
By adhering to regulations like GDPR, organizations can build a strong foundation for cybersecurity, safeguarding sensitive information and mitigating the risk of data breaches.
Role of Cybersecurity Audits
- Cybersecurity audits are crucial for organizations to assess their compliance with regulations and identify any gaps in their security measures.
- These audits help in evaluating the effectiveness of cybersecurity controls, detecting vulnerabilities, and ensuring that data protection laws are being followed diligently.
- Regular cybersecurity audits not only enhance compliance but also reinforce the importance of maintaining robust cybersecurity practices in digital identity management.
Epilogue
In conclusion, prioritizing cybersecurity in digital identity management is not just a necessity but a crucial step in safeguarding sensitive information online. Stay informed, stay protected.
Questions and Answers
How does cybersecurity protect digital identities?
Cybersecurity safeguards digital identities by implementing measures like encryption, secure authentication, and regular security audits.
What are the consequences of inadequate cybersecurity in digital identity management?
Inadequate cybersecurity can lead to identity theft, data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage.
How do emerging technologies like blockchain impact cybersecurity in digital identity management?
Blockchain enhances security by providing decentralized and tamper-proof records, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and fraud.
Why is compliance with regulations like GDPR important for cybersecurity in digital identity management?
Compliance ensures that data protection laws are followed, reducing the risk of cyber threats and maintaining trust with users.
What are the best practices for securing digital identities against cyber threats?
Best practices include using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, keeping software updated, and educating users on cybersecurity awareness.